forked from logzhan/RobotKernal-UESTC
3.3 KiB
3.3 KiB
UWB 定位原理
1.三维坐标转二维坐标
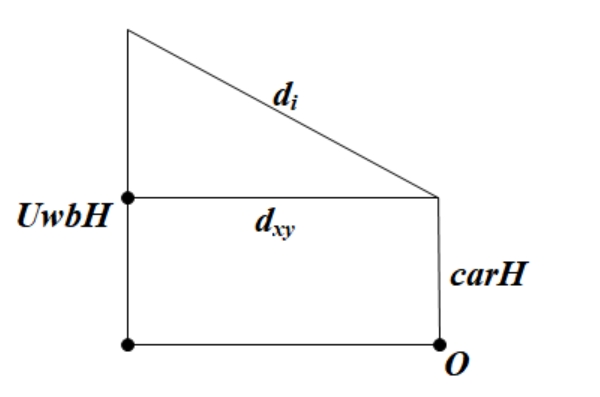
在割草机器人项目中,割草机器人目前只考虑二维平面的定位。但是UWB测量的距离是三维距离,所以我们根据机器人的高度carH和UWB标签的高度UwbH计算出水平距离dxy。
// dxy^2 = di^2 - (UwbH = carH)^2
for(int i=0; i<3; i++){
this->d[i] = sqrt(this->d[i] * this->d[i] - (AnchorPos[i][2] - CARHEIGHT) *
(AnchorPos[i][2] - CARHEIGHT));
}
2.多项式拟合
UWB的定位是存在波动的,所以会根据UWB计算距离的规律对计算的距离进行多项式拟合,可以起到滤波提高精度作用。下面的计算实际是收集不同实测距离下,UWB的实际输出距离,利用3次多项式拟合得到的结果。
下面的计算跟标签的位置以及高度无关,主要跟UWB的硬件设备的特性有关。
d[0] = ((((4.9083e-07 * d[0]) - 4.6166e-04) * d[0]) + 1.0789) * d[0] + 5.4539;
d[1] = ((((-4.1679e-07 * d[1]) + 5.0999e-04) * d[1]) + 0.7930) * d[1] + 29.8296;
d[2] = ((((2.3514e-07 * d[2]) - 1.8277e-04) * d[2]) + 0.9935) * d[2] + 9.8852;
3.位置求解
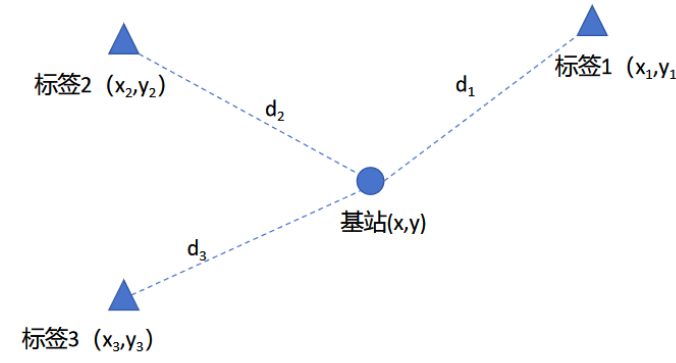
UWB位置求解采用如下图示:
UWB的定位可以用下面公式描述, 其中(x,y)是割草机器人上面的UWB的位置,另外三个坐标点是3个UWB标签的位置,可以有如下的公式。
d_1^2 = (x_1 - x)^2 + (y_1 - y)^2 \space\space\space\space\space (1)\\
d_2^2 = (x_2 - x)^2 + (y_2 - y)^2 \space\space\space\space\space(2)\\
d_3^2 = (x_3 - x)^2 + (y_3 - y)^2 \space\space\space\space\space(3)\\
(2)-(1)以及(3)-(2)消去二次项,可得:
d_1^2 - d_2^2 = \left[ -2(x_1 - x_2)x + x_1^2 - x_2^2 \right] + \left[ -2(y_1 - y_2)y + y_1^2 - y_2^2 \right] \\
d_1^2 - d_3^2 = \left[ -2(x_1 - x_3)x + x_1^2 - x_3^2 \right] + \left[ -2(y_1 - y_3)y + y_1^2 - y_3^2 \right]
整理为矩阵形式:
-2 \begin{bmatrix}
x_1 - x_2 & y_1 - y_2 \\
x_1 - x_3 & y_1 - y_3
\end{bmatrix}
\begin{bmatrix}
x \\
y
\end{bmatrix}
=
\begin{bmatrix}
(d_1^2 - d_2^2) - (x_1^2 - x_3^2) - (y_1^2 - y_3^2) \\
(d_1^2 - d_3^2) - (x_1^2 - x_3^2) - (y_1^2 - y_3^2)
\end{bmatrix}
整理可得:
\begin{align*}
A &= -2\cdot \begin{bmatrix}
x_1 - x_2 & y_1 - y_2 \\
x_1 - x_3 & y_1 - y_3
\end{bmatrix}\\
b &= \begin{bmatrix}
(d_1^2 - d_2^2) - (x_1^2 - x_2^2) - (y_1^2 - y_2^2) \\
(d_1^2 - d_3^2) - (x_1^2 - x_3^2) - (y_1^2 - y_3^2)
\end{bmatrix}\\
X &= \begin{bmatrix}
x\\
y
\end{bmatrix}
\end{align*}
矩阵A对应的代码:
for(int i=0; i<2; i++){
A.mat[i][0] = -2*(this->AnchorPos[0][0]-this->AnchorPos[i+1][0]);
A.mat[i][1] = -2*(this->AnchorPos[0][1]-this->AnchorPos[i+1][1]);
}
矩阵b对应的代码:
for(int i=0; i<2; i++)
{
b.mat[i][0] = (this->d[0]*this->d[0]-this->d[i+1]*this->d[i+1])\
- (this->AnchorPos[0][0]*this->AnchorPos[0][0]-this->AnchorPos[i+1][0]*this->AnchorPos[i+1][0])
- (this->AnchorPos[0][1]*this->AnchorPos[0][1]-this->AnchorPos[i+1][1]*this->AnchorPos[i+1][1]);
}
那么,上述矩阵可以通过X=(A^T\cdot A)^{-1}A^T*b 求解UWB的位置。
Mat AT=~A;
uwbPos=(AT*A)%AT*b;
this->uwb_data_.x_ = uwbPos.mat[0][0];
this->uwb_data_.y_ = uwbPos.mat[1][0];